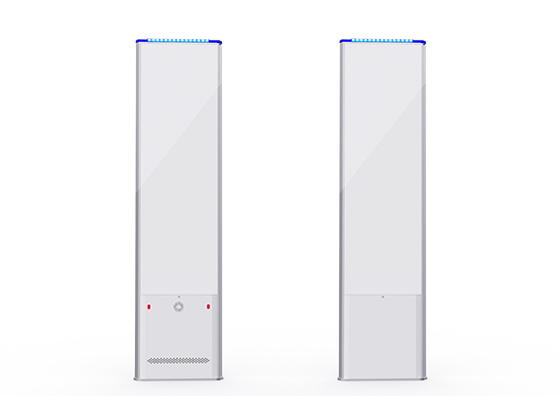
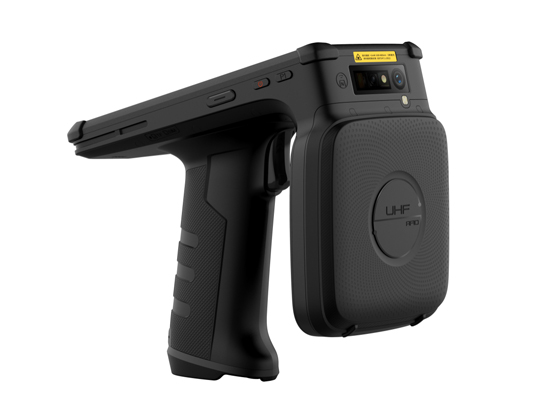
The library is an important base for learning and getting knowledge. The library is mostly the collection of thousands of books, journals and electronic resources to help students. As the need for libraries to function effectively increases, the introduction of advanced technologies is inevitable. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) revolutionized library collection management, security, and inventory management. RFID technology simplifies processes, minimizes effort, and improves convenience.

Understanding RFID in Libraries
The RFID technology used in the library mainly consists of three elements:
1. RFID tags: These are installed inside materials such as books CDs and keep data secure like title, author name, item status, etc. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not need to be scanned directly.
2. RFID reader: They receive the RFID signal from the tag and track it using the library database.
3. Library Management Software: They Integrate with RFID systems to record check-in, check-out, and inventory management in real-time.
In addition, the system integrates with library management software to ensure smooth tracking and reporting of library assets.
Benefits of RFID technology in libraries
1. Faster check-in and check-out
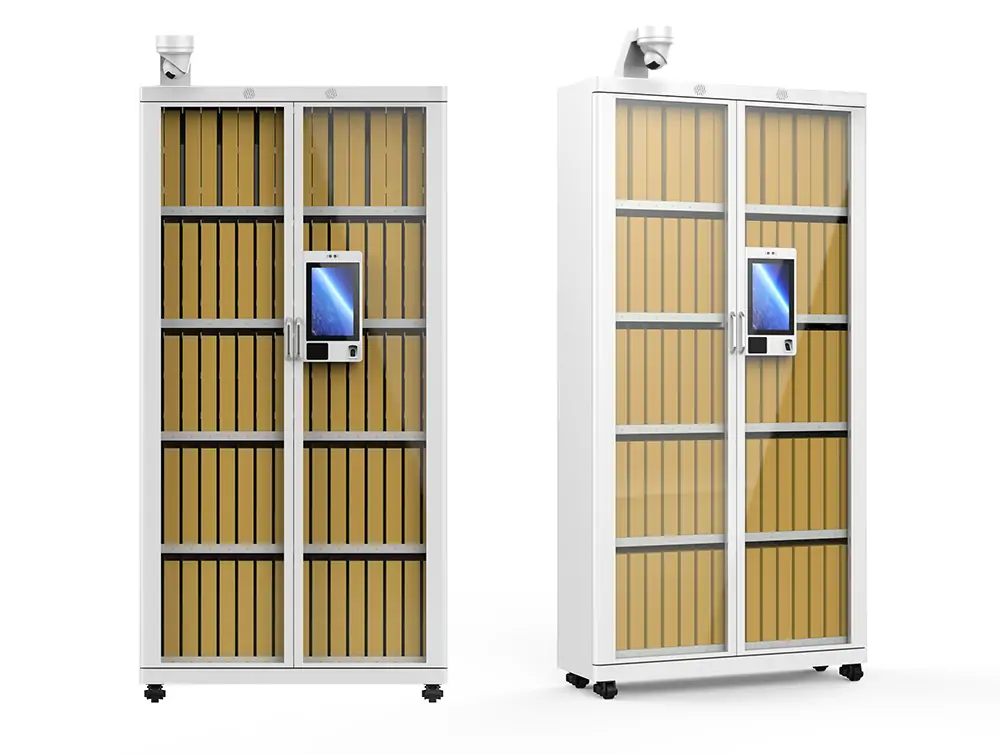
RFID automates the lending and return process. When library users place many books on the self-service kiosk's RFID reader, the system instantly registers each item. This eliminates manual scanning, reduces long lines, and improves service speed.
The RFID-compatible return box instantly registers the return as soon as the book is deposited
This reduces the time for the library database to be updated in real-time and for the next borrower to use the book.
2. Improve inventory management
Managing thousands of books and materials is a challenge. RFID streamlines this process by assisting workers to scan several books simultaneously with a mobile RFID reader. Rather than scanning each barcode manually, personnel can proceed down the aisle while the scanner picks up RFID tags in real-time.
This makes regular inventory faster and more accurate. Libraries are now able to perform inventory checks more frequently, misplaced books are easily located and promptly re-shelved
3. Security and loss prevention
In library management, loss is caused by forgotten books and theft. RFID enhances security by integrating with entrance and exit sensors. When someone tries to bring items out without proper checkout, the system warns. This feature reduces theft and ensures that the collection stays within the library collection.
In addition, the RFID system can be programmed to send staff automatic alerts if the book is placed in the wrong section or removed from the specified area.
4. Reduce manual labor
Previously, a lot of time was wasted on lending, check-in, and stock management. RFID automates the process, enabling staff to focus on answering visitors, collection management, and event planning. The transition from repetitive work to more substantial work enhances overall efficiency and job satisfaction among library staff.
5. Simplify book sorting
The sorting of returned books is another labor-intensive task in the library. RFID-enabled sorting systems automatically classify books. When a user puts a book in the return box, the RFID reader identifies it and uses a belt conveyor to guide it to the appropriate section.
This reduces the work burden of the staff and improves the availability of other borrowers as books are quickly re-shelved.
6. Improve user experience
The library introduces self-service kiosks, allowing visitors to borrow or return books without the help of staff. This convenience makes library use more efficient, especially at peak times.
In addition, RFID-equipped search stations allow users to find books by displaying the exact location of the shelves. This saves time and reduces frustration when searching for specific materials.
7. Integration with digital and multimedia collections
Modern libraries manage not only printed books but they also have digital books. Most provide online content like e-books, audio books, and DVDs for easy use. Digital materials are also managed with the help of RFlD technology so that security and safety can be maintained.
It helps proper management of digital book with co-existing traditional books.
A few libraries employ RFID-enabled smart cards, where users can borrow physical materials as well as digital content. This will ensure hassle-free lending experience and encourage the utilization of different materials.
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
RFID has many advantages, but it requires careful planning to install it. Libraries must consider multiple factors like cost, system compatibility, and staff training to maximize benefits.
1. Initial Investment Cost
RFID technology requires purchasing tags, readers, self-service kiosks, and software. Initial investments can be large, but many libraries recover costs by improving efficiency, reducing losses, and improving services.
2. Training and adaptation of staff
Library personnel must undergo training to effectively use the RFID system. This includes:
● RFID reader and self-service kiosk operation
● Troubleshooting technical issues
● Support for users unfamiliar with technology
Training allows staff to maximize the benefits of RFID while maintaining quality services for visitors.
3. Compatibility with existing systems
Most libraries already use the Integrated Library System (ILS) for inventory creation and distribution. Ensuring that RFID solutions work seamlessly with these existing platforms is critical for smooth migration.
Libraries should choose RFID providers that offer flexible integration options to avoid interruptions in their daily operations.
4. Privacy and Data Security
RFID tags store privacy data when intercepted. Libraries must introduce encryption and access control to protect sensitive information. In addition, a policy is required to maintain the confidentiality of the user's loan history and prevent access by unauthorized parties.
Future of RFID in Libraries
As technology grows, RFID technology will continue to strengthen its library operations. New trends include:
Mobile RFID solution: Enables real-time scanning and tracking with mobile devices, making inventory management even more efficient.
Smart shelves: Shelves with RFID sensors automatically update the position of books and reduce forgetting.
Cloud-based integration: More libraries adopt a cloud-based library management system that works seamlessly with RFID, enabling remote monitoring and data analysis.
RFID compatible library cards: By incorporating RFID chips into library cards, some facilities allow users to borrow books with one card, access to digital content, and enter restricted areas.
Conclusion
RFID changed the operation of the library by streamlining core processes such as check-in, check-out, inventory management, and security. This technology dramatically reduces manual labor, improves accuracy of operations and improves user experience.
Initial implementation requires cost and training, but in the long term, RFID is a valuable investment for today's library. By incorporating this technology, the library can provide users with a more reasonable and convenient experience while maintaining an internal structure for the future.